Product Discovery Workshop - Step-By-Step Guide for Software Projects
In this article, we will go into the details of what a discovery workshop is, what are its main goals, who...

Yes, you read that right. Failing to conduct advanced research on your target audience and potential customers is one of the top five reasons startups fail.
Our confidence in this statement stems from a recent study conducted by renowned entrepreneur Bill Gross, the co-founder of Pacific Investment Management Co. In-depth market and marketing research provides budding companies with insights into critical aspects such as launch timing, unique features to include, and more, allowing them to plan their launch effectively.
In 2019, the failure rate of startups was around 90%. The research concludes 21.5% of startups fail in the first year, 30% in the second year, 50% in the fifth year, and 70% in their 10th year.
According to business owners, reasons for failure include money running out, being in the wrong market, a lack of research, bad partnerships, ineffective marketing, and not being an expert in the industry.
source: www.investopedia.com
So before you try to soar in your business field, you must understand the art and science behind startup market research. It is with this goal in mind that we present the following article.
In this article:
In essence, market research is a business strategy applied at the very beginning of conceptualizing a business idea, which involves acquiring a thorough understanding of the target market, its dynamics, the attitudes of potential customers, the buying behavior of focus groups, and other important factors.
The results of market research are used to make business-oriented decisions and plan the launch accordingly. When done and implemented with the desired diligence, market research holds the power to leverage the success of a startup.
Market research is so widespread it has become one of the fastest-growing industries in the world, surpassing the $74.3 billion mark in 2019. While market research is crucial for any business, it plays a particularly important role for an early-stage startup, ensuring its victorious launch and increasing the chances of long-term success.
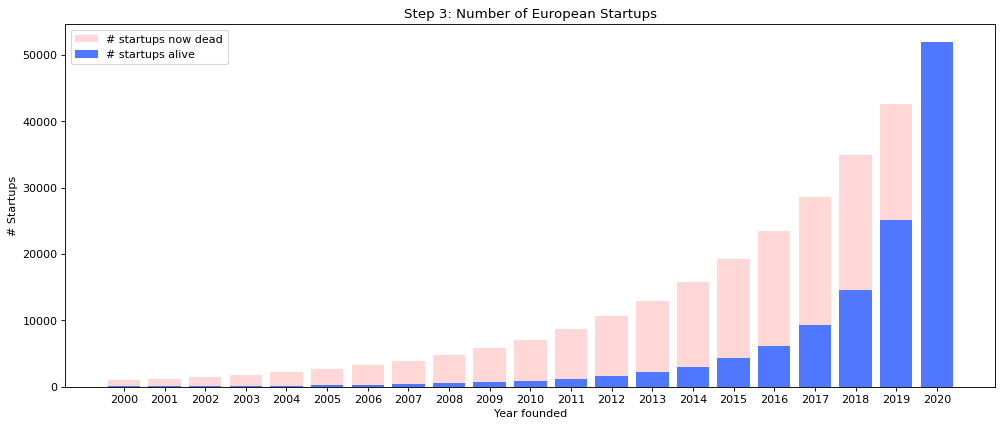
The statistic illustrates the harsh reality of founding a startup. Most of the new companies fail. The good news is that entrepreneurs’ belief in their success is stronger than statistics. That’s why new companies are created all the time. || source: https://medium.com/glassdollar/estimating-the-number-of-startups-in-europe-5d28286307f8
Market research is one of the few viable ways for companies to improve their decision-making and survive in today’s competitive world. It’s used to ensure the best results from the efforts invested in product development, marketing, and service expansion.
While planning to conduct market research, it is crucial to know its types. Here are the two most common:
Primary research is conducted either by the startup itself or by a third party and involves collecting data by engaging directly with customers. The information is gathered by asking relevant questions. It’s the most common type of research.
Primary market research is best suited for startups that:
Based on research requirements, startups list relevant questions and interact directly with customers.
In addition, it’s always a good idea to gather customer insights on your direct competitors and the latest trends employed by other small businesses.
During the exploratory primary research phase, most startup owners collect feedback on their businesses through surveys, scouring online forums related to their target market, and conducting one-on-one interviews with potential customers.
Example: Digital service-delivery surveys you receive after using a service.
Secondary research is conducted by analyzing data collected by a third party that has no direct involvement with the startup and its customers. Usually, all research begins with secondary research, as it doesn’t require any direct investment.
Through secondary market research for startups, you can figure out:
Example: The government-ordained public studies on a particular area/domain can be called secondary research studies for the market.
Brainstorming, feasibility analysis, and critical thinking can be your few cost-effective ways to derive success from market insights data.
Many businesses mistakenly believe they know their market solely based on anecdotal evidence, yet the landscape is often far more nuanced and dynamic than they realize. Proper market research doesn’t just validate assumptions; it unravels misconceptions and casts a guiding light on uncharted territories. This process is not merely about data collection but about sculpting a clearer, evidence-backed vision. CEO, ASPER BROTHERS Let's Talk
Conducting market research is a tedious task for many.
Startups face additional challenges during market research due to limited investment, resources, and talent. However, excelling in market research is possible, and you can start by paying close attention to the points we mention below.
Why: Every research initiative should start with a clear understanding of its purpose. Without a purpose, your efforts can scatter, and results may not be actionable.
How: You should outline your specific objectives. For example, are you trying to validate a new product idea? Understand shifts in consumer behavior? Explore potential markets?
Why: The research methodology will shape the type of insights derived.
How: Evaluate your objectives. Quantitative research (surveys, structured interviews) yields structured, numerical data. Qualitative research (focus groups, open-ended interviews) offers deeper, nuanced insights.
Why: You need a clear understanding of who your customers are to provide meaningful solutions.
How: Create detailed customer personas. These are semi-fictional representations of ideal customers based on real data and market insights.
Why: By asking the right questions, you’re able to gather relevant data.
How: Prioritize questions or areas of investigation that align directly with the research purpose. Some of the key questions to include:
Why: Tools facilitate data collection, analysis, and visualization. The right tools streamline the process.
How: For surveys, platforms like SurveyMonkey or Google Forms can be used. Analytics tools like Google Analytics or Tableau are great for data analysis.
Google Alerts, Google Trends, Simpleweb, Statista, and Ahrefs are a few tools to help learn industry and brand-specific trends.
Why: Ensures that the tools used are effective and capture intended information.
How: Run a mini-version of your study with a small group, tweak based on feedback, then proceed to the main study.
Why: There’s a wealth of existing information that can be leveraged to inform decisions.
How: Explore industry reports, competitor analysis, and existing market studies. Tools like Statista or industry-specific publications can be invaluable.
Why: This adds credibility to your findings and ensures they’re accurate and reflective of reality.
How: Revisit some respondents for clarifications, or cross-check findings with secondary sources.
Why: Raw data must be turned into actionable insights.
How: Depending on the methodology, data can be statistically analyzed, charted, or interpreted through themes in qualitative feedback. To organize this process, decide on the KPIs to base your analysis on those KPIs. Present the gathered and analyzed data in a report.
Why: Markets, consumer behavior, and technologies evolve. Research should too.
How: Set periodic reviews of previous research. Reassess the market situation and adjust strategies accordingly.
Why: Ensures everyone in the team is aligned with market understandings.
How: Host meetings or workshops to discuss findings. Use visual aids like charts, graphs, and presentations for clarity.
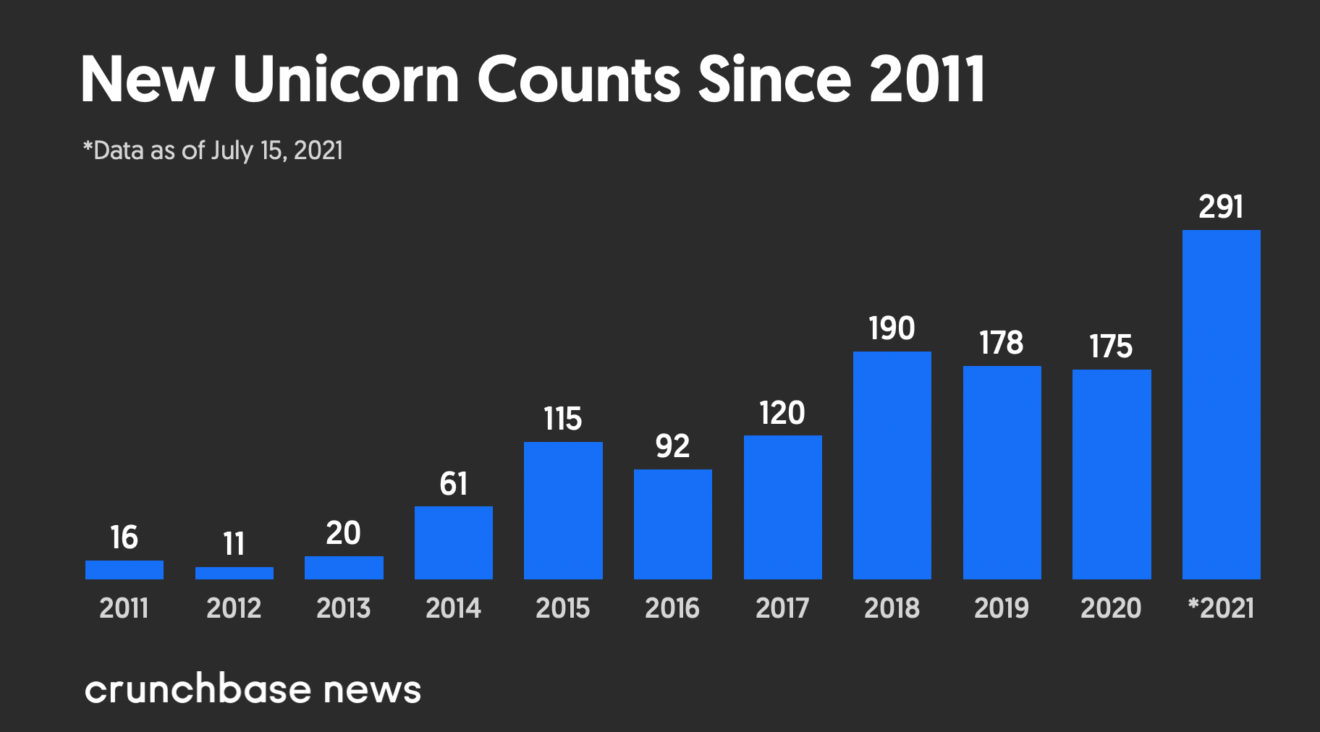
2021 is a record year for new unicorns, companies valued at more than $1 billion. || Source: https://news.crunchbase.com/news/unicorn-startup-investors-2021-tiger-global/
The process of analysis is like translating raw data into a compelling story—one that informs, guides, and ultimately drives strategic decision-making. Proper analysis not only illuminates what’s happening but also why it’s happening.
So, how should startups approach this analysis, and who should be involved?
Before diving into specific methods, it’s essential to differentiate the two main types of data:
Quantitative data provides a measurable and numeric insight into the behavior, opinions, and patterns of your target market. Whether obtained from structured survey questions, website analytics, or sales figures, these numbers provide clarity and objectivity. Quantitative analysis often falls into two primary categories:
Descriptive statistics offer a summarized overview of the main aspects of data:
Visual tools like histograms, bar graphs, and pie charts can also be part of descriptive statistics, offering visual representations of these metrics.
While descriptive statistics describe a data set, inferential statistics make predictions or inferences about a population based on a sample. Here are the key methods:
Qualitative data analysis seeks to understand underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations. Techniques include:
The analysis is often a collaborative effort. Depending on the complexity and scope, consider involving:
To truly appreciate the power and importance of comprehensive market research, you should look at the most successful businesses today. Their achievements often stem directly from insights derived from meticulous market research.
The 5 examples we list below underscore the fundamental truth in business: understanding your market is pivotal. When companies listen, adapt, and innovate based on research, they set themselves on a path to sustained success.
An online platform that connects travelers with local hosts offering their spaces for accommodation. It revolutionized the hospitality industry by offering unique and personalized lodging experiences worldwide.
A Danish company renowned for its iconic interlocking plastic bricks. These construction sets have sparked creativity in both children and adults, making Lego a household name in the toy industry.
An American streaming service that offers a wide array of TV shows, movies, documentaries, and more. Initially a DVD-by-mail service, Netflix transitioned to streaming and later to producing original content, becoming a dominant force in the entertainment industry.
A personal care brand owned by Unilever. It’s best known for its moisturizing soap, but its product range includes deodorants, body washes, shampoos, and more. Dove has also been recognized for its marketing campaigns that challenge conventional beauty standards.
A global fast-food chain known for its burgers, fries, and the Golden Arches. Founded in the U.S., McDonald’s expanded worldwide, adapting its menu to local tastes and becoming one of the most recognizable brands globally.
The landscape of market research has, over the decades, transformed from mere number crunching to a sophisticated blend of art and science. As we stand on the precipice of a future punctuated by AI-driven insights, augmented reality market simulations, and even neuroscience in consumer understanding, startups must recognize the boundless possibilities ahead.
However, amid this whirlwind of technological advancements, the essence remains the same: understanding people. The tools and techniques will evolve, but the quest to connect, empathize, and serve the ever-changing needs of the market will always be at the heart of successful entrepreneurship.
As startups chart their course in this vast sea of opportunities, the compass of well-conducted market research will be more crucial than ever.

In this article, we will go into the details of what a discovery workshop is, what are its main goals, who...
An accurate cost estimate is the key to a successful software development project. This may sound a bit cliché – but we...
So what makes product strategy so essential? And what are the principal components of a digital product strategy? Let's take...